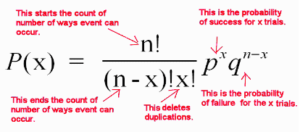
Binomial distribution: When the population under observation can be divided into two distinct groups, one with a certain characteristic of the observations and the rest without this characteristic, the distribution of the occurrence of the characteristic in the population is defined by the Binomial Distribution.
As an example, in a given population, if it is required to define the distribution of prevalence of a certain disease, then the entire population can be divided into two groups, one with the disease and other without the disease. If the probability of a person having the disease is p and not having the disease is q (that is, 1-p), then the distribution of various probabilities, that is, the probability of finding none, one, two, three, four,… persons with the disease in a group of n persons is given by the successive terms of the binomial distribution (q + p)n.
The expression (q+p)n is given by